How to Describe Ascites in Physical Exam
The puddle sign may be present when as little as 120 mL of fluid is present. Pancreatic ascites is a somewhat rare entity that results from a pancreatic duct injury leading to persistent leakage of pancreatic secretions into the peritoneum.
Core Concepts Diagnosis And Management Of Ascites Management Of Cirrhosis Related Complications Hepatitis C Online
There are several physical examination maneuvers described for detection of ascites described below that are at least moderately sensitive and specific.

. 120-250 ml Mild ascites Fullness of flanks. We retrospectively reviewed discharges from 1983 to 2010 to select patients whose records included a diagnosis of ascites. Mild ascites is hard to notice but severe ascites leads to abdominal distensionPeople with ascites generally will complain of progressive abdominal heaviness and pressure as well as shortness of breath due to mechanical impingement on the diaphragm.
Symptoms and signs of. This condition is usually diagnosed by physical examination. KEEP YOUR FINGERS THERE.
Thyroid may be enlarged. Several conditions and diseases can lead to ascites for example abdominal cancer liver cirrhosis tuberculosis and congestive heart failure. Physical examination of patients with ascites is usually remarkable for flank dullness shifting dullnes and fluid wave.
Samples of peritoneal fluid should be sent to the laboratory for protein concentration specific. Consider signs of other uncommon etiologies of ascites. Recent studies in terminal cancer patients have correlated five.
Percentage of patients with ascites usually on the right side. Assessing Possible Ascites. 1000-1500 ml fluid Moderate ascites Fluid thrill.
Ascites caused by cancer most often occurs with advanced or recurrent cancer of the ovary bladder colon breast pancreas or lung and with lymphomas. The clinical significance of ascites is based largely on its etiology. 2000 ml fluid Tense ascites Quantitative Assessment of Edema.
Abdominal exam techniques compliment each other. This can lead to ascites accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity. Various maneuvers can confirm this findingref14.
Ascitic fluid volume abdominal diaphragm and wall elasticity and the splanchnic organs are all. Ascites is detected with physical examination of the abdomen by visible bulging of the flanks. The severity of this condition varies widely and is often dependant on the location and degree of ductal injury and any infection in the fluid.
Ascites Observe distention bulging flanks Palpationno evidence of mass Palpation fluid wave Enlarged liver hepatomegaly Percussion indicates extension of liver below diaphragm Palpation confirms location of. ASCITES-increase in NO in the splanchnic circulation -- vasodilation -- activation of RAAS -- Na and water retention -- ascites 1 portal HTN no ascites. If youre a newer nurse practitioner chances are you may find documentation a challenge especially if you dont have an electronic medical records system prompting the input of your physical exam findings.
This is due to the presence of a diaphragmatic defect that allows ascitic fluid to pass into the pleural cavi ty. Medical practitioners use the clinical term tense ascites to describe a palpatory discovery of large fluid volume ascites. Moderate vasodilation 3 refractory ascites.
Ascites is a condition in which fluid collects in spaces within the abdomen. Tongue enlarged macroglossia peri-orbital edema delayed peripheral deep tendon reflexes delay most prominent in return phase of reflex exam Degenerative arthritis of extremities usually hands and fingers especially affected are PIPs of the middle and ring. No single maneuver is both highly sensitive and specific.
When peritoneal fluid exceeds 500 mL ascites may be demonstrated by the presence of shifting dullness or bulging. FREE How To Describe Abdominal Exam. Documentation is key to continuity of care for your patients as well as to protecting yourself should questions arise about the patient encounter.
Although the most common cause of ascites is cirrhosis of the liver cancer accounts for about 10 percent of ascites cases. When peritoneal fluid exceeds 500 mL ascites may be demonstrated by the presence of shifting dullness or bulging flanks. Updated on 2 Jul 2020.
Abdominal exam techniques compliment each other. Therefore at least two maneuvers are necessary to increase the accuracy of physical exam for ascites. Physical examination PE provides practical clinical information for prognosis and symptom assessment which may improve communication and decision-making regarding palliative therapies disposition and whether family members wish to remain at bedside.
Ascites is a medical condition involving the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. Because ascitic fluid characteristically sinks with gravity while gas-filled loops of bowel float to the top percussion gives a. .
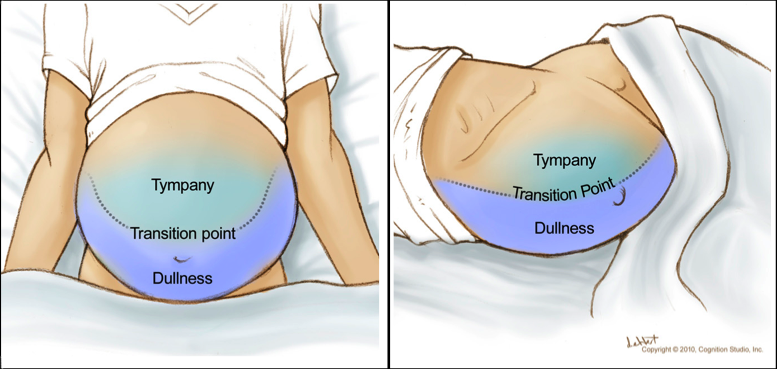
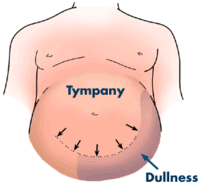
Dullness along the flanks while in the supine position may indicate the presence of ascites. You should hear tympany from air in the loops of bowel that have floated up. Physical exam findings in patients with ascites are as followings.
Begin percussing in the center or most protuberant part of the abdomen. A fluid-wave sign is notoriously inaccurate. Elevated jugular venous.
Shifting Dullness with Ascites. Portal vein hypertension results from increased resistance to blood flow through an inflamed and fibrotic liver. Ascites Observe distention bulging flanks Palpationno evidence of mass Palpation fluid wave Enlarged liver hepatomegaly Percussion indicates extension of liver below diaphragm Palpation confirms location of lower edge also detects contour texture.
Percuss laterally towards you from that point till you encounter dullness. Signs of Ascites Increase in abdominal girth and weight gain Everted umbilicus Scrotal edema Bulging flanks when patient lying supine. The presence of decreased breath sounds or dull percussion in lower chest on physical examination is diagnostic of pleural effusion beside ascites.
Medically ascites is defined as fluid accumulation in the peritoneal cavity. The aim of our study was to describe the changing prevalence demographic features etiologies and treatment of ascites in children hospitalized during a 27-year period at the Johns Hopkins Hospital Baltimore MD. Skin dry with brittle hair.
Severe vasodilation a diuretic intractibleintolerant 80. Ascites physical exam involves checking the patient for physical symptoms of fluid accumulation. A protuberant abdomen with bulging flanks suggests the possibility of ascitic fluid.
500 ml fluid. This can often be determined by the history and physical examination but paracentesis is diagnostic.
Techniques Liver Ascites Exam Physical Diagnosis Skills University Of Washington School Of Medicine

Ascites Physical Exam Diagnostic Accuracy Sensitivity Grepmed

Shifting Dullness To Detect Ascites On Physical Exam 1 Grepmed
No comments for "How to Describe Ascites in Physical Exam"
Post a Comment